
整理一些平常常用的信息收集小脚本
nmap结合mascan识别存活主机
nmap用来识别存活,然后将输出给masscan,masscan对存活ip的端口进行扫描,扫描完后通过对扫描结果过滤,输出ip:port的形式,然后通过httpx去进一步识别存活。
#nmap扫描存活
nmap -sn 172.29.130.0/24 > nmap-ip.txt
#获取nmap扫描存活的ip
cat nmap-ip.txt | grep "repo" | cut -d " " -f6 | cut -d "(" -f2 | cut -d ")" -f1 > ip.txt
#masscan扫描端口
sudo masscan -iL ip.txt --rate 10000 -p1-65535 --only-open
#获取masscan扫描结果中的ip
cat masscan-ip.txt | grep "tcp" | cut -d " " -f 4,6 | awk '{print $2,$1}'| tr " " ":" | cut -d "/" -f1 | cut -d ":" -f1 | sort -t "." -k4n | uniq > ip.txt
#获取masscan扫描结果中的端口
cat masscan-ip.txt | grep "tcp" | cut -d " " -f 4,6 | awk '{print $2,$1}'| tr " " ":" | cut -d "/" -f1 | cut -d ":" -f2 | sort -n | uniq > port.txt
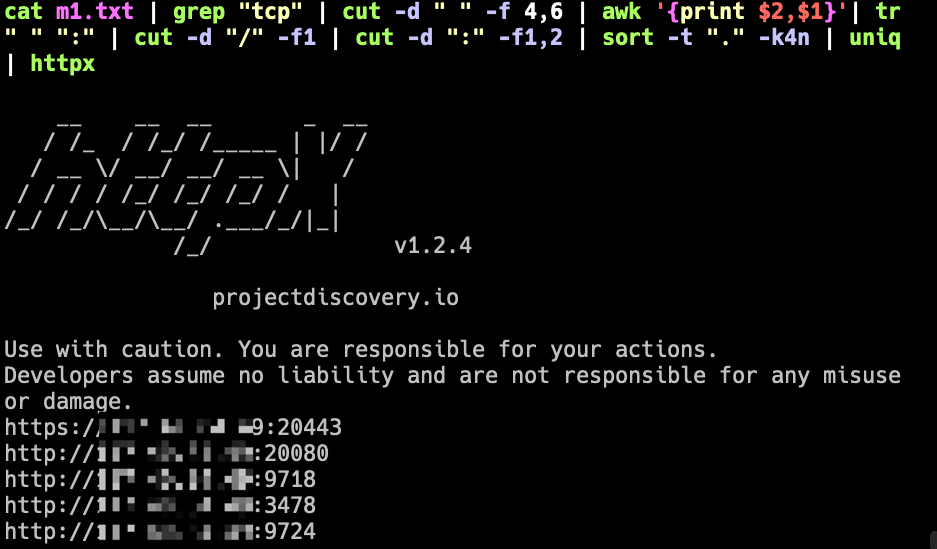
#即要端口,又要ip的话
cat m.txt | grep "tcp" | cut -d " " -f 4,6 | awk '{print $2,$1}'| tr " " ":" | cut -d "/" -f1 | cut -d ":" -f1,2 | sort -t "." -k4n | uniq
整理出ip:port格式(192.168.1.1:8080)后可以使用其他工具扫描系统是否存活,通过httpx查看系统是否存活
格式大概这样,就可以获取完整的url了。
windows下批量识别存活主机
# windows下批量ping C段,识别存活
for /L %i IN (1,1,254) DO ping -w 2 -n 1 192.168.1.%i
ip范围生成
# 192.168.1.1-192.168.1.254
# usage: 1 254 192.168.1.
for i in {$1..$2};do echo "$3"$i;done
向文本中批量追加特定内容
如有一个文本,每行都有一个ip,需要在每个ip前面加上http协议,变成http://ip,就需要批量在每行前面追加内容,用到的命令是sed命令,替换字符分别是`$`和`^`号,`$`代表每行末尾,`^`代表每行开头。
# bash下,向文件的每行末尾添加特定的内容,此处是ip,例如:192.168.1.x,转换后为192.168.1.0/24
cat ip.txt | sed 's/$/.0\/24/'
# bash下,向文件的每行开头添加特定的内容,此处是ip,例如:192.168.1.5,转换后为http://192.168.1.5
cat ip.txt | sed 's/^/http:\/\//'
获取内网段所有网关ip
获取内网段所有网关ip,用来判断C段是否存活
#A段
for i in {1..255};do for b in {1..255};do echo "10".$i.$b."1";done;done
#B段
for i in {16..31};do for b in {1..255};do echo "172".$i.$b."1";done;done
#C段
for i in {1.255};do echo "192.168".$i."1";done
从文件中提取ip
grep -E -o "([0-9]{1,3}[\.]){3}[0-9]{1,3}" file.txt
从文本中提取url
grep -E -o "https?://[a-zA-Z0-9./?=_-]*" file.txt
#从js文件中提取url
curl https://abc.com/file.js | grep -Eo "(http|https)://[a-zA-Z0-9/?=_=]*"*
从apk中提取url
参考:GitHub - ndelphit/apkurlgrep: Extract endpoints from APK files
apkurlgrep -a path/to/file.apk
子域名收集
curl -s "https://rapiddns.io/subdomain/jxuspt.com?full=1#result" | grep "<td><a" | cut -d "/" -f3 | cut -d '"' -f1 | xargs -l2 | sed 's/#result//g' curl -s "https://rapiddns.io/subdomain/$1?full=1" | grep '<td>[a-z]' | cut -d "<" -f2 | cut -d ">" -f2 | grep -v http | sort
ssh key搜索
for key in ~/.ssh/*; do ssh-keygen -l -f "${key}"; done | uniq
查看wifi密码
netsh wlan show profile name ="WIFI_5G"
netsh wlan show profile name ="WIFI_5G" key=clear
指纹识别小脚本
根据前面的一些内容,可以写一些bash脚本,方便一键查询,下面的脚本目的是进行masscan扫描,然后httpx探测存活,kscan和observer_ward扫描系统指纹。
结合.bash_profile文件,只要输入mscan 11.11.11.11即可开始扫描

#!/bin/bash
# masscan port scan
#
#
echo -e "\033[31m 开始masscan端口扫描... \033[0m"
sudo masscan -p1-65535 $1 --rate 1000 > ./mport.txt
echo -e "\033[31m 开始httpx存活探测... \033[0m"
cat mport.txt | grep "tcp" | cut -d " " -f 4,6 | awk '{print $2,$1}'| tr " " ":" | cut -d "/" -f1 | cut -d ":" -f1,2 | httpx > mresult.txt
rm -rf ./mport.txt
echo -e "\033[31m kscan扫描中... \033[0m"
if [ -f "mresult.txt" ]; then
kscan -t mresult.txt -o kscanresult.txt
fi
echo -e "\033[31m 指纹识别中... \033[0m"
if [ -f "kscanresult.txt" ]; then
cat kscanresult.txt | grep -E "http:|https" | awk 'BEGIN {FS=" " } ; { print $1 }' | observer_ward --stdin
fi
rm -rf kscanresult.txt
Drag and drop your files here
Loading comments...
Source