JSX 的本质
JSX 到底是什么,我们先来看看 React 官网给出的一段定义:
JSX 是 JavaScript 的一种语法扩展,它和模板语言很接近,但是它充分具备 JavaScript 的能力。
对于 JSX,facebook 定义为“语法扩展”,同时充分具备JS 的能力。但事实上人家长得和 HTML 很像,并不像熟知的 JavaScript,这怎么解释呢?
JSX 语法和 JavaScript 关系
实际上答案很简单 ,见React 官网
JSX 会被编译为 React.createElement(), React.createElement() 将返回一个叫作“React Element”的 JS 对象。
所以说其实 JSX 是会通过一次编译后,通过React.createElement()的调用变成一个React Element的 js 对象。
那么编译是如何做到的呢?其实对于ECMAScript 2015+ 版本的代码,我们通常需要使用一个工具Babel来对旧版本的浏览器做兼容。
比如ES2015+中很好用的模板字符串语法糖:
var text = 'World'
console.log(`Hello ${text}!`) //Hello World!
Babel 就可以帮我们把这段代码转换为大部分低版本浏览器也能够识别的 ES5 代码:
var text = 'World'
console.log('Hello'.concat(text, '!')) //Hello World!
类似的,Babel 也具备将 JSX 语法转换为 JavaScript 代码的能力。 那么 Babel 具体会将 JSX 处理成什么样子呢?【例子】
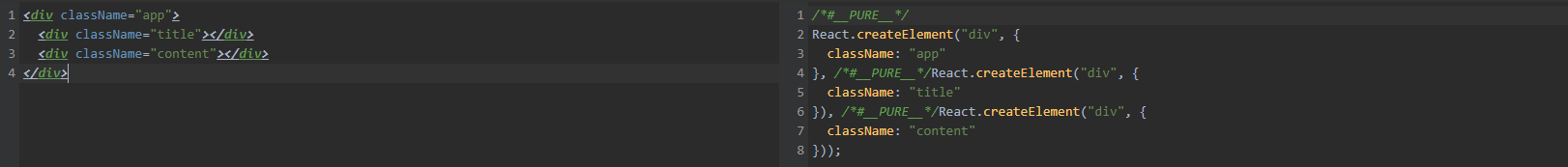
可以看到,JSX 的标签都被转化成了对应的 React.createElement 调用,所以说实际上 JSX 就是写的 React.createElement,所以说它看起来像 HTML,但内核是 JS 罢了。
JSX 的本质是 React.createElement 这个 JavaScript 调用的语法糖,这也就完美地呼应上了 React 官方给出的“JSX 充分具备 JavaScript 的能力”这句话。
如上图,JSX 的优势很明显,JSX 代码层次分明,嵌套关系清晰;但是使用 React.createElement 看着就比 JSX 混乱的多,读起来不友好,写起来也费劲。
JSX 语法糖允许前端开发者使用我们最为熟悉的类 HTML 标签语法来创建虚拟 DOM,在降低学习成本的同时,也提升了研发效率与研发体验。
JSX 是如何映射为 DOM 的?
先来看看 createElement 源码,这里是一段抄来的有注释的源码
export function createElement(type, config, children) {
var propName
//提取保留名称
var props = {}
var key = null
var ref = null
var self = null
var source = null
//标签的属性不为空时 说明标签有属性值 特殊处理:把key和ref赋值给单独的变量
if (config != null) {
//有合理的ref
if (hasValidRef(config)) {
ref = config.ref
}
//有合理的key
if (hasValidKey(config)) {
key = '' + config.key
}
self = config.__self === undefined ? null : config.__self
source = config.__source === undefined ? null : config.__source
//config中剩余属性,且不是原生属性(RESERVED_PROPS对象的属性),则添加到新props对象中
for (propName in config) {
if (hasOwnProperty.call(config, propName) && !RESERVED_PROPS.hasOwnProperty(propName)) {
props[propName] = config[propName] //config去除key/ref 其他属性的放到props对象中
}
}
}
// Children can be more than one argument, and those are transferred onto
// the newly allocated props object.
// 子元素数量(第三个参数以及之后参数都是子元素 兄弟节点)
var childrenLength = arguments.length - 2
if (childrenLength === 1) {
props.children = children
} else if (childrenLength > 1) {
var childArray = Array(childrenLength) //声明一个数组
//依次将children push到数组中
for (var i = 0; i < childrenLength; i++) {
childArray[i] = arguments[i + 2]
}
{
//冻结array 返回原来的childArray且不能被修改 防止有人修改库的核心对象 冻结对象大大提高性能
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(childArray)
}
}
props.children = childArray //父组件内部通过this.props.children获取子组件的值
}
//为子组件设置默认值 一般针对的是组件
//class com extends React.component 则com.defaultProps获取当前组件自己的静态方法
if (type && type.defaultProps) {
//如果当前组件中有默认的defaultProps则把当前组件的默认内容 定义到defaultProps中
var defaultProps = type.defaultProps
for (propName in defaultProps) {
if (props[propName] === undefined) {
//如果父组件中对应的值为undefined 则把默认值赋值赋值给props当作props的属性
props[propName] = defaultProps[propName]
}
}
}
{
//一旦ref或者key存在
if (key || ref) {
//如果type是组件的话
var displayName =
typeof type === 'function' ? type.displayName || type.name || 'Unknown' : type
if (key) {
defineKeyPropWarningGetter(props, displayName)
}
if (ref) {
defineRefPropWarningGetter(props, displayName)
}
}
}
//props:1.config的属性值 2.children的属性(字符串/数组)3.default的属性值
return ReactElement(type, key, ref, self, source, ReactCurrentOwner.current, props)
}
参数分析
function createElement(type, config, children)拥有三个参数type, config, children对应的含义
type:用于标识节点的类型。它可以是类似“h1”“div”这样的标准 HTML 标签字符串,也可以是 React 组件类型或 React fragment 类型。
config:以对象形式传入,组件所有的属性都会以键值对的形式存储在 config 对象中。
children:以对象形式传入,它记录的是组件标签之间嵌套的内容,也就是所谓的“子节点”“子元素”。
比如下面的调用示例
React.createElement(
'ul',
{
// 传入属性键值对
className: 'list',
// 从第三个入参开始往后,传入的参数都是 children
},
React.createElement(
'li',
{
key: '1',
},
'1'
),
React.createElement(
'li',
{
key: '2',
},
'2'
)
)
它对应的 DOM 结构如下
<ul className="list">
<li key="1">1</li>
<li key="2">2</li>
</ul>
了解参数过后继续往下走
拆解 config 参数
if (config != null) {
//有合理的ref
if (hasValidRef(config)) {
ref = config.ref
}
//有合理的key
if (hasValidKey(config)) {
key = '' + config.key
}
self = config.__self === undefined ? null : config.__self
source = config.__source === undefined ? null : config.__source
//config中剩余属性,且不是原生属性(RESERVED_PROPS对象的属性),则添加到新props对象中
for (propName in config) {
if (hasOwnProperty.call(config, propName) && !RESERVED_PROPS.hasOwnProperty(propName)) {
props[propName] = config[propName] //config去除key/ref 其他属性的放到props对象中
}
}
}
此处将入参的 config 拆解成ref, key, self, source, props几个属性,紧接着就是处理 children 的部分
提取子元素
从上面分解 config 之后是处理子元素的代码,此处将第二个参数以后的所有参数都存入props.children数组
// Children can be more than one argument, and those are transferred onto
// the newly allocated props object.
// 子元素数量(第三个参数以及之后参数都是子元素 兄弟节点)
var childrenLength = arguments.length - 2
if (childrenLength === 1) {
props.children = children
} else if (childrenLength > 1) {
var childArray = Array(childrenLength) //声明一个数组
//依次将children push到数组中
for (var i = 0; i < childrenLength; i++) {
childArray[i] = arguments[i + 2]
}
{
//冻结array 返回原来的childArray且不能被修改 防止有人修改库的核心对象 冻结对象大大提高性能
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(childArray)
}
}
props.children = childArray //父组件内部通过this.props.children获取子组件的值
}
接下来就是处理当父组件给 children 传入 props 情况,如果子组件设置了默认值并且父组件未传入 props(即值为undefined) 时使用提供的默认值。
//为子组件设置默认值 一般针对的是组件
//class com extends React.component 则com.defaultProps获取当前组件自己的静态方法
if (type && type.defaultProps) {
//如果当前组件中有默认的defaultProps则把当前组件的默认内容 定义到defaultProps中
var defaultProps = type.defaultProps
for (propName in defaultProps) {
if (props[propName] === undefined) {
//如果父组件中对应的值为undefined 则把默认值赋值赋值给props当作props的属性
props[propName] = defaultProps[propName]
}
}
}
下面将检测key和ref是否被赋值,如果有那么就会执行defineKeyPropWarningGetter和defineRefPropWarningGetter两个函数,随后将一系列组装好的数据传入ReactElement中
此处defineKeyPropWarningGetter和defineRefPropWarningGetter两个函数的作用是让 ref 和 key 在被获取的时候报错
ReactElement
createElement()最终调用的方法,其实ReactElement()方法只是将传入的一系列数据增加一些诸如type、source、self等标记属性然后直接返回一个 js 对象。
JSX 中的使用的类似 html 的节点,在 Babel 的帮助下,转换为嵌套的 ReactElement 对象,这些信息对于后期构建应用的树结构时非常重要的,而 React 通过提供这些类型的数据,来脱离平台的限制。